We rely on our sense of hearing in our day-to-day lives. With healthy hearing abilities, we can maintain sound conversations every day, as well as navigate the world and be aware of our surroundings. We often take our hearing ability for granted and start realising its importance when it starts to fade. Let’s begin valuing this gift of God and take precautionary measures to protect our hearing every day, preserving our natural hearing abilities for a lifetime, or as long as we can!
Addressing Hearing Loss
Millions of people in India suffer from some kind of hearing loss, irrespective of age and gender. Hearing problems affect not only the patient but also their family members and friends, who struggle to talk to them, even during simple conversations. Individuals with hearing difficulties find it challenging to hear certain high-frequency speech sounds, like the ‘s’, ‘f’, and ‘th’ sounds. It often results in misunderstanding and frustration, particularly when the hearing-impaired individual asks others to repeat themselves.
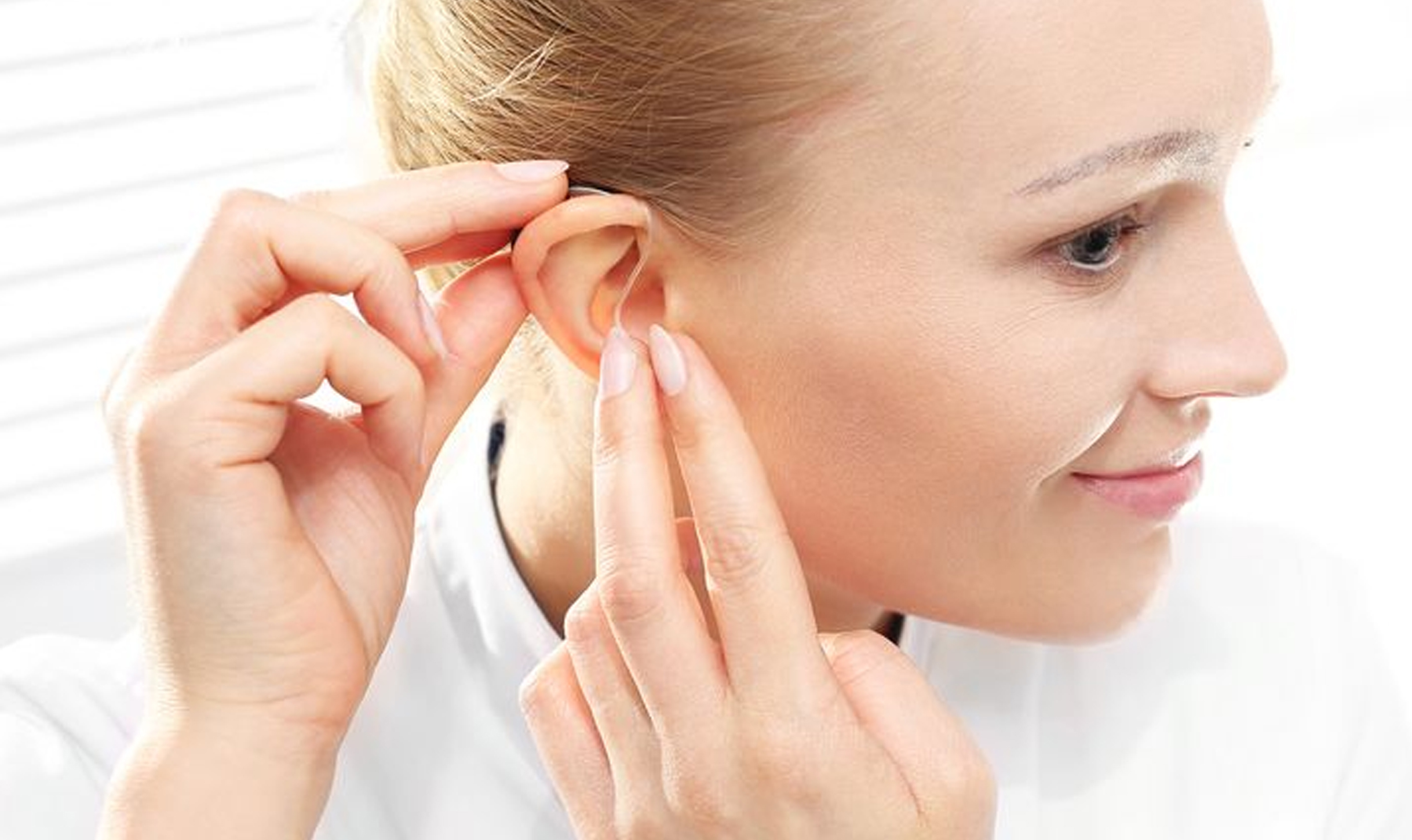
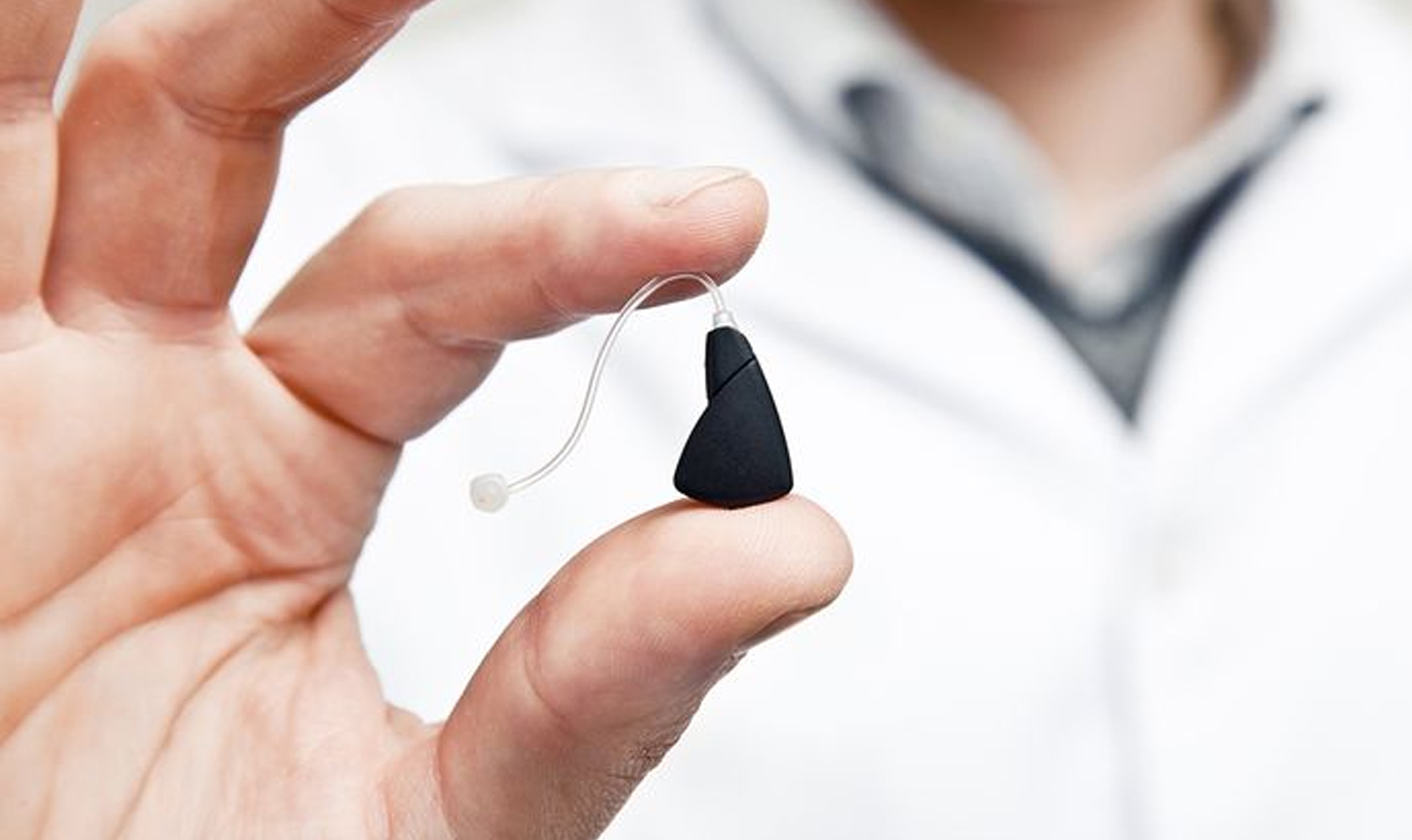
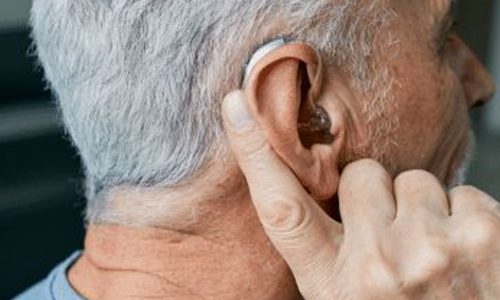
Thanks to smart hearing aids for coming as a permanent solution to hearing loss. Today’s digital hearing aids are packed with advanced programming features and automated technologies designed to treat a range of hearing problems. Modern hearing aids and other assistive listening devices also help improve the sound quality and offer comfortable fits to maximise the hearing experience for the user. Treat your hearing loss problems promptly to prevent further decline in your hearing ability and communication, and to minimise the risks of cognitive issues, like dementia.
Know Your Ears
The human ear is a complex yet fascinating organ that enables us to hear and be aware of our surroundings and maintains our body balance and posture. The anatomy of the ear helps us to understand its different parts, how it works, and why we must take care of it.
The human ear has three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Each component plays a unique function in the overall hearing process.
Outer Ear
- Pinna or Auricle: The Pinna is the visible, outer part of the ear that captures the sound waves. It acts as a funnel and channels the sound waves toward the ear canal.
- Ear Canal: The Ear Canal, also known as the External Auditory Canal, is a tube-like pathway that transmits the sound waves from the pinna to the eardrum. The earwax of the ear canal protects the inner ear from dirt, debris, and bacteria.
Middle Ear
- Tympanic Membrane or Eardrum: This thin membrane vibrates every time sound waves strike it. It acts as a barrier between the outer and middle ear, protecting the delicate components within.
- Ossicles: The ossicles are a group of three small bones - the malleus (hammer), the incus (anvil), and the stapes (stirrup). They amplify the sound vibrations and transmit them to the inner ear.
- Eustachian Tube: It is a narrow tube connecting the middle ear to the throat. It regulates and equalises ear pressure with the outside environment.
Inner Ear
- Cochlea: This spiral-shaped organ comprises tiny hair cells that convert mechanical sound vibrations into electrical signals.
- Semicircular Canals: These three fluid-filled canals help detect rotational movements of the head.
- Auditory Nerve: It transmits the converted electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain, where these are processed and interpreted as meaningful sounds.
- Vestibule: It contains two otolith organs (utricle and saccule), which, along with the semicircular canals, help detect linear acceleration and spatial orientation. It helps the brain maintain balance and posture, particularly during motion, thus preventing falls.
How Does Our Sense of Hearing Work?
Next, the brain processes and interprets the sound by analysing the pitch, tone, volume, timbre, and spatial location. The auditory cortex of the brain’s temporal lobe is responsible for processing these sound signals. It also differentiates between different sounds, such as music, speech, and noise. That’s when we can actually hear, and the entire hearing process occurs within a fraction of a second.